Animal species affected
The species presented here are particularly frequent victims of illegal killings. Discover detailed descriptions of the individual species, including their characteristic identifying features, endangerment and conservation status and the most common methods of illegal killing.
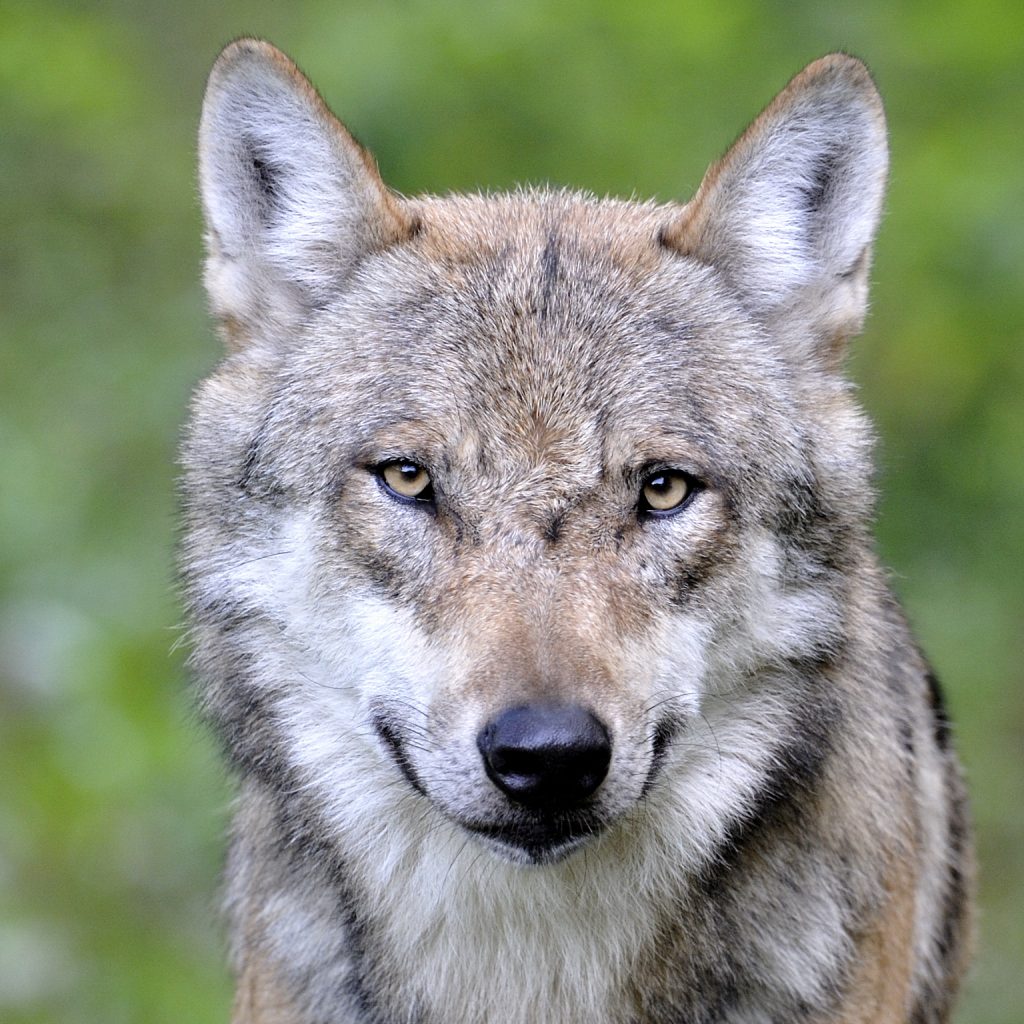

Wolf
Canis lupus
After a long period of extinction caused by humans, the wolf is returning from the east and has been re-establishing itself in Germany for 20 years and in Austria for a few years now. In the 2022/2023 monitoring year, 184 packs, 46 pairs and 22 territorial individuals were recorded in Germany. There are 6 packs in Austria. Wolves live in family groups (packs), which usually consist of a parent pair, the young of the last two years and the pups. They are mainly crepuscular and nocturnal.
Illegally killed wolves in Germany
This graph shows the number of illegally killed wolves per year in Germany, based on confirmed cases. However, the actual number of unreported cases is likely to be considerably higher. (Source: DBBW – Dokumentations- und Beratungsstelle des Bundes zum Thema Wolf)
Illegally killed wolves in Austria
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
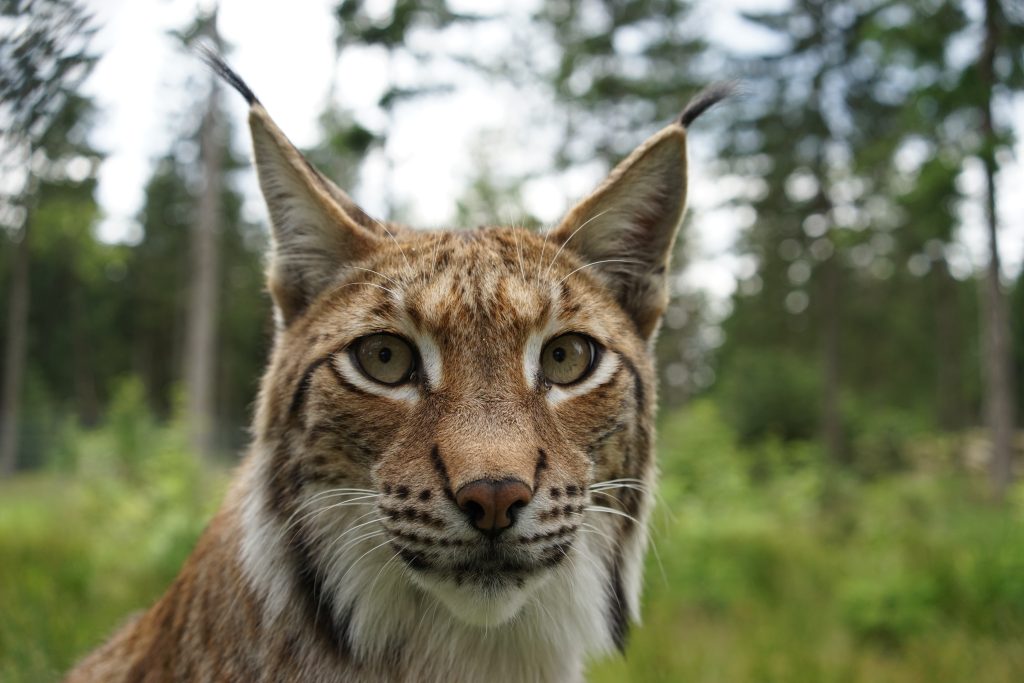

Lynx
Lynx lynx
The lynx is the largest European cat species. After the species was wiped out at the end of the 19th century, almost 200 individuals are now living in Germany and around 40 animals in Austria thanks to reintroduction projects. Their preferred habitat are forests of any composition. Lynx are nocturnal and crepuscular solitary animals that usually only meet during the mating season. During their nocturnal forays, they can cover up to 40 kilometres.
Illegally killed lynxes in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed lynxes in Austria
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
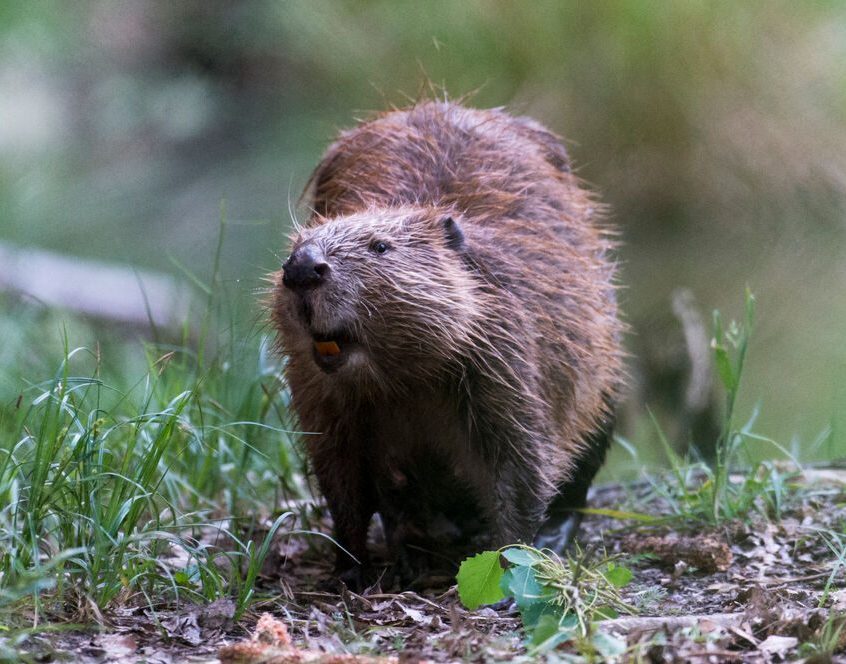

Beaver
Castor fiber
The beaver is the largest European rodent and was on the verge of extinction for a long time. There are now over 40,000 animals living in Germany again, and around 9,000 individuals in Austria. Beavers inhabit both flowing and standing waters – preferably surrounded by forests. As ecosystem engineers, they strongly shape their habitat and are known for building so-called beaver lodges in which they live in family groups. They are active at dusk and at night.
Illegally killed beavers in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed beavers in Austria
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
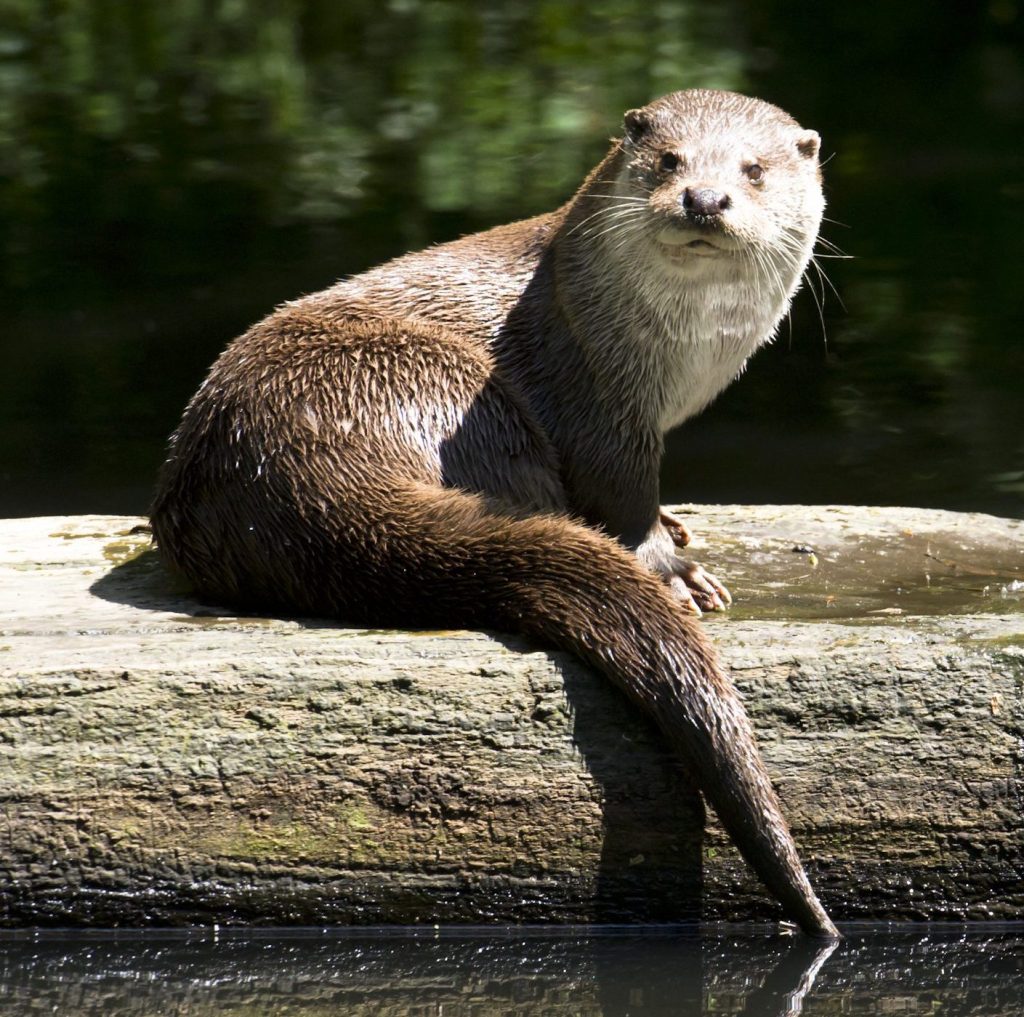

Eurasian otter
Lutra lutra
Otters are members of the marten family that are perfectly adapted to both water and land life. Rivers, marshes, swamps, fjords, sea coasts as well as high mountain and lowland lakes are among their habitats. They are mainly crepuscular and nocturnal, but can also be found as solitary animals during the day. They seek shelter in riverbank caves, under the roots of old trees or in muskrat burrows.
Illegally killed otters in Germany
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed otters in Austria
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
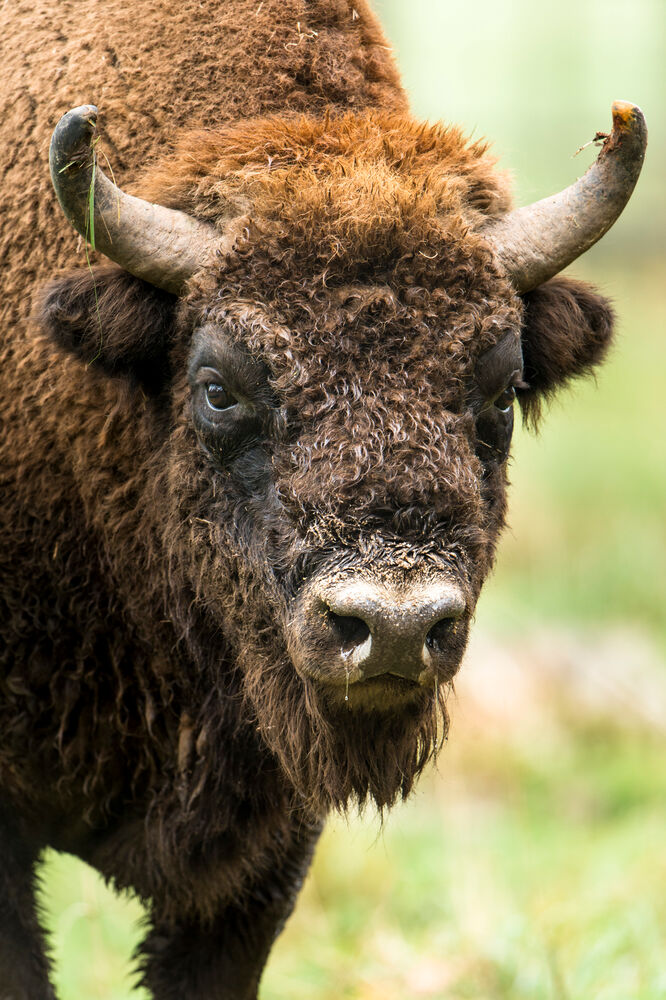
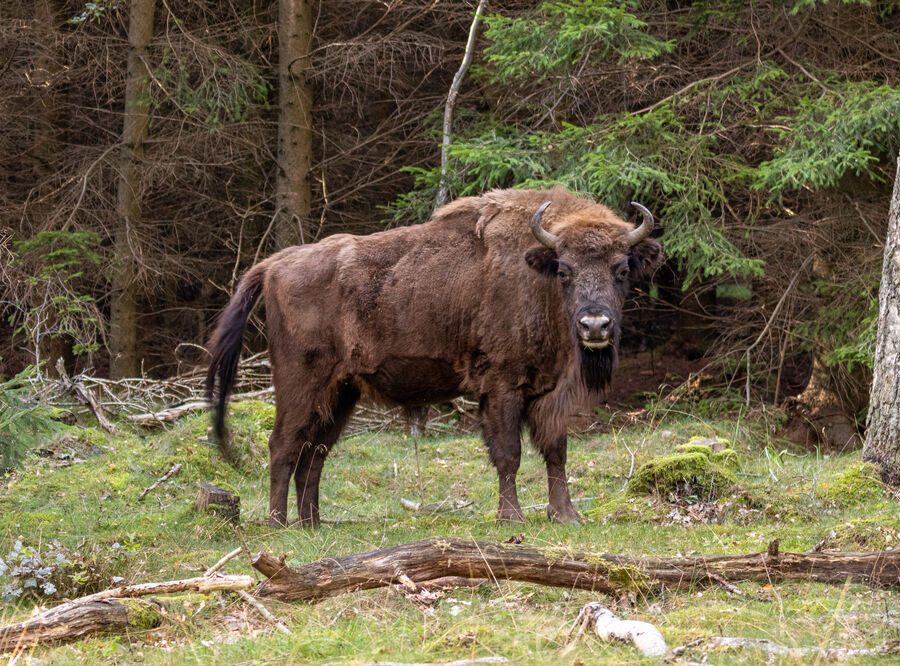


European bison
Bison bonasus
The European bison is a relative of the American bison and the largest land mammal in Europe. There is only a very small population in Germany; Eastern Europe has the main populations. The cloven-hoofed animals inhabit structurally rich landscapes consisting of deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests as well as clearings, pastures and meadows. European bison mainly form herds, only older bulls live solitary lives. They do not have typical territories, but live in large roaming areas that can overlap.
Illegally killed bison in Germany
To date, two bison have been illegally shot in Germany.
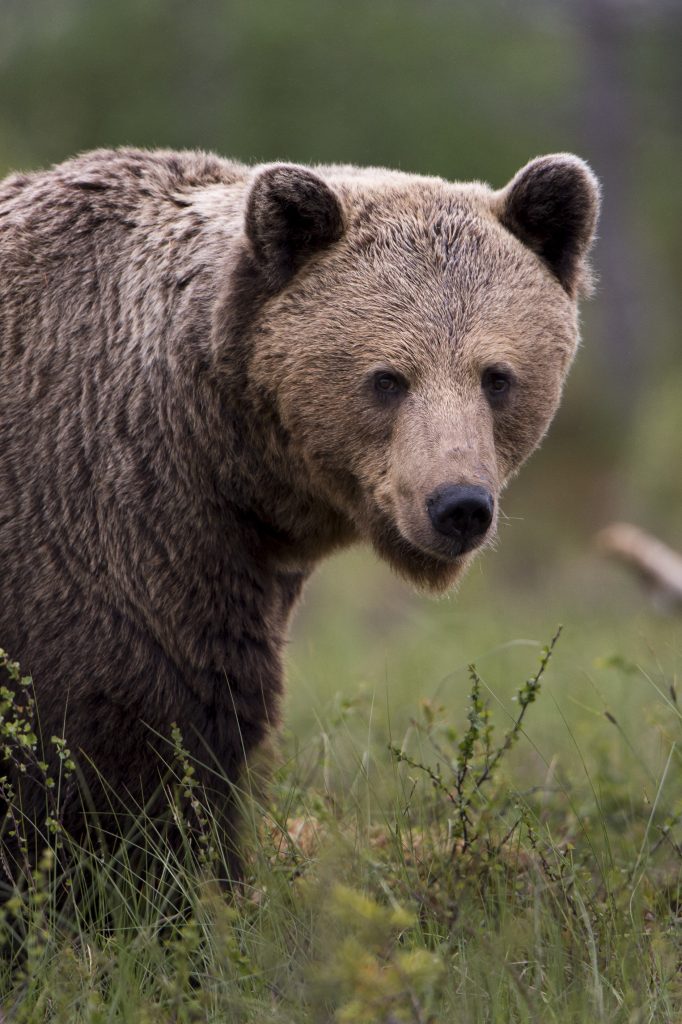
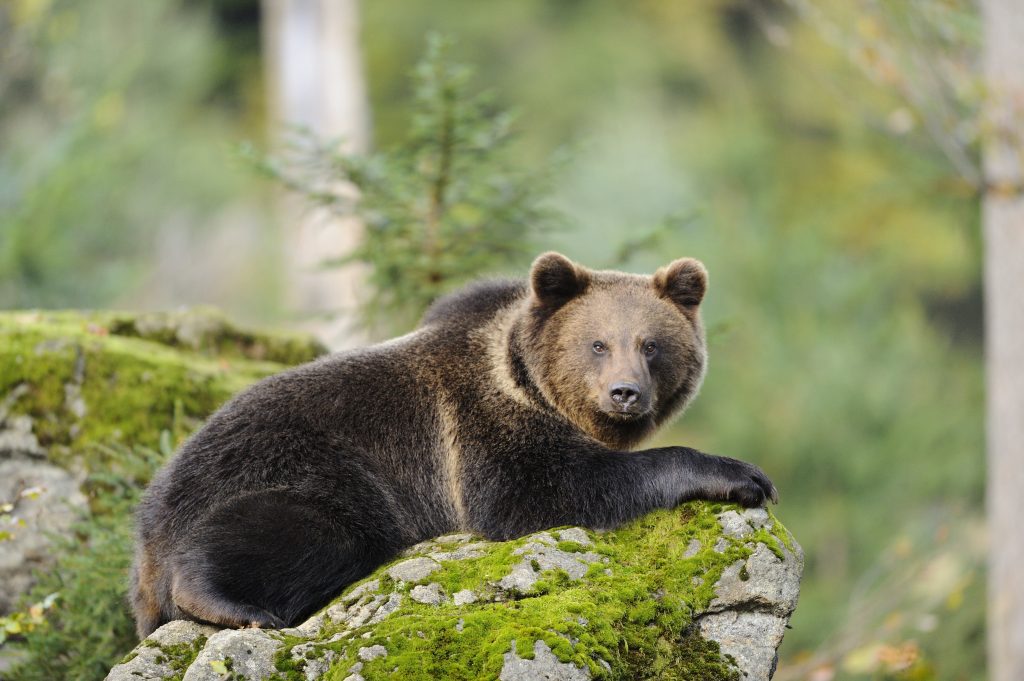


Brown bear
Ursus arctos
European brown bears are the second largest bears in the world and the largest predators in Europe. Once widespread throughout the continent, the animals are now only found in very few regions. In Central Europe, they inhabit forests in valleys and mountain regions. There is no existing population in Germany or Austria. However, there are occasional crossings of Austrian-Italian or Slovenian individuals into Austria or Bavaria. There are 2 – 3 brown bears in Austria (2018-2020), while there are around 80 individuals in the Alps (2019). European brown bears tend to be nocturnal, which may be due to human activity. They hibernate in winter, live solitary lives and have no fixed territories.
Illegally killed brown bears in Germany
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed brown bears in Austria
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
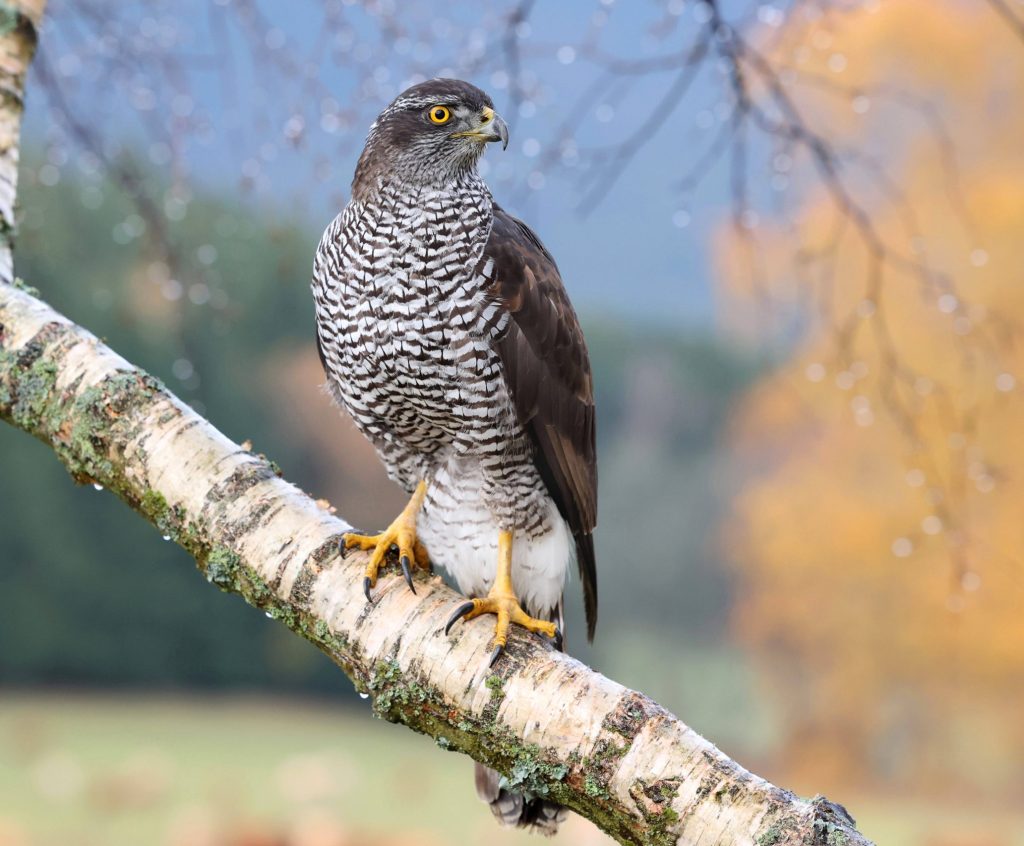
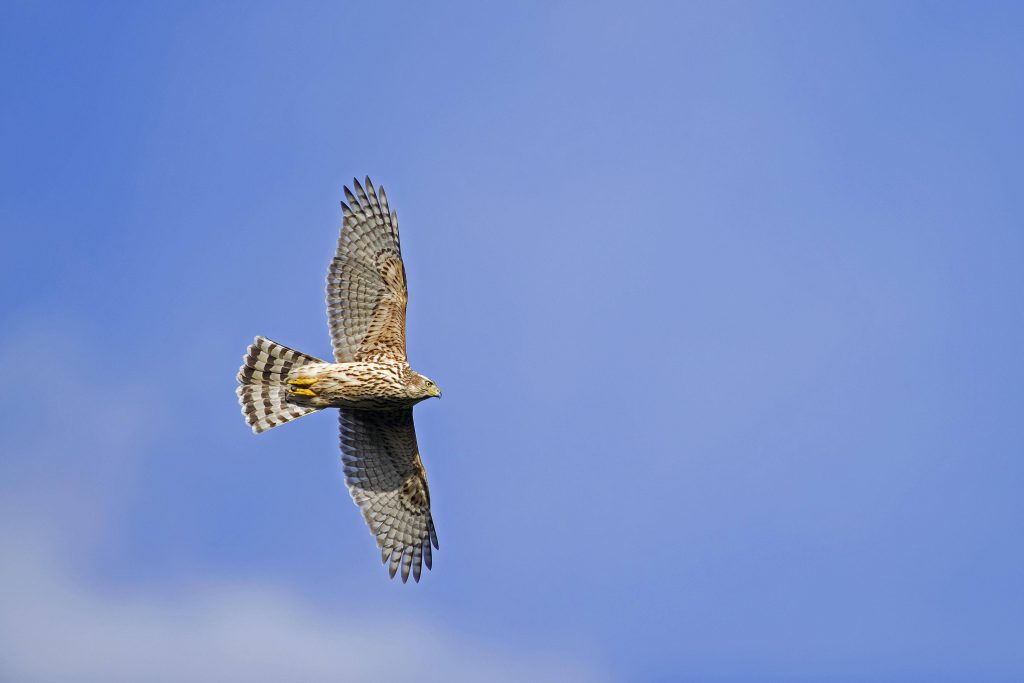


Eurasian Goshawk
Accipiter gentilis
The goshawk is one of the most frequently persecuted birds of prey in Germany and is found in almost all of Europe. The birds inhabit forests, meadows and increasingly also cities. Goshawks form permanent breeding pairs, but outside the breeding phase the animals live separately. They defend their territories intensively and, as resident birds, usually remain in them all year round.
Trapping (with hawk trapping baskets)Illegally killed hawks in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed hawks in Austria
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
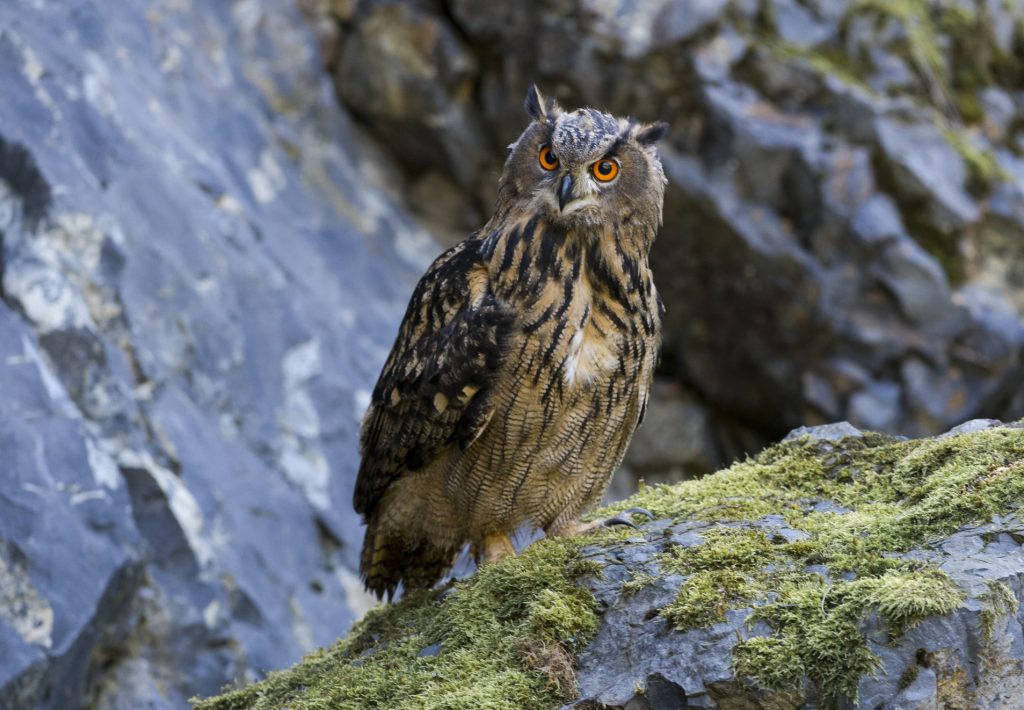
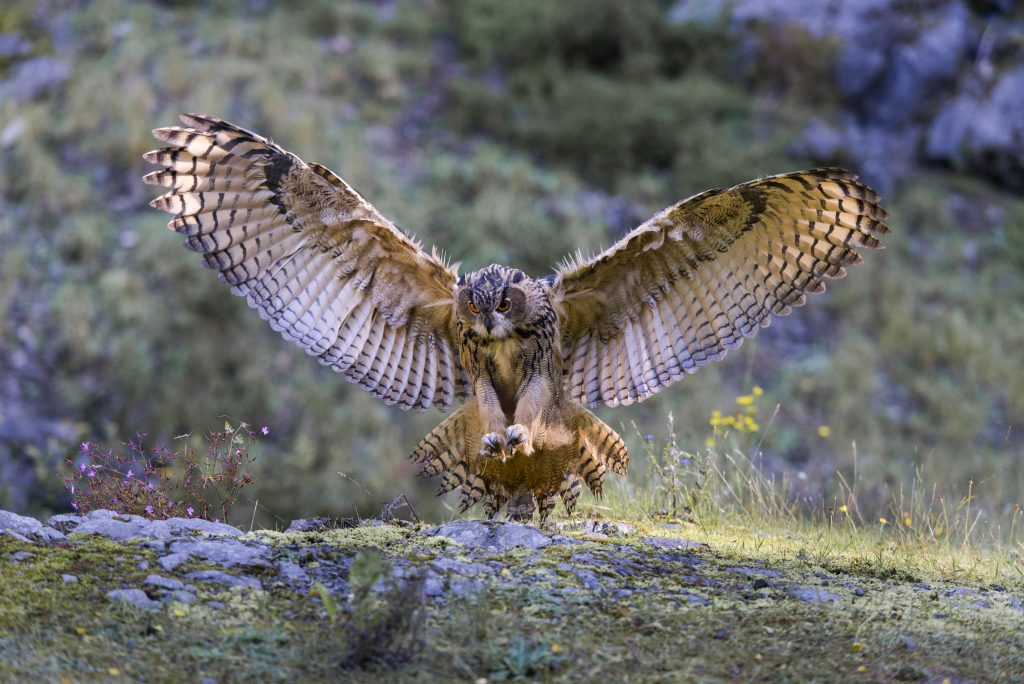


Eurasian eagle-owl
Bubo bubo
The eagle owl is the largest owl in Europe. In Central Europe, the species inhabits forests and fields and prefers to breed in relatively inaccessible rock faces or quarries. In Germany there are up to 1,000 breeding pairs, in Austria it is assumed that there are 360 to 530 breeding pairs. The animals are nocturnal and excellent hunters. As resident birds, they do not migrate in winter and intensively defend the narrower area around their nest.
Illegally killed eagle owls in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed eagle owls in Austria
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
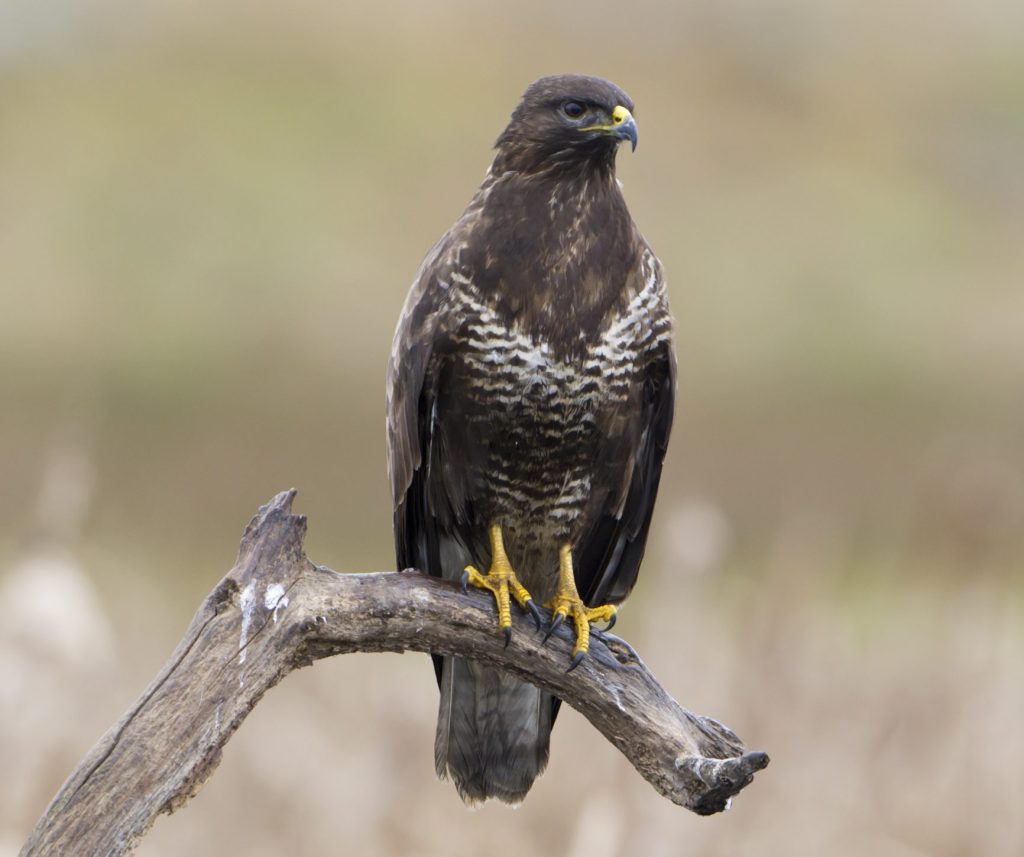

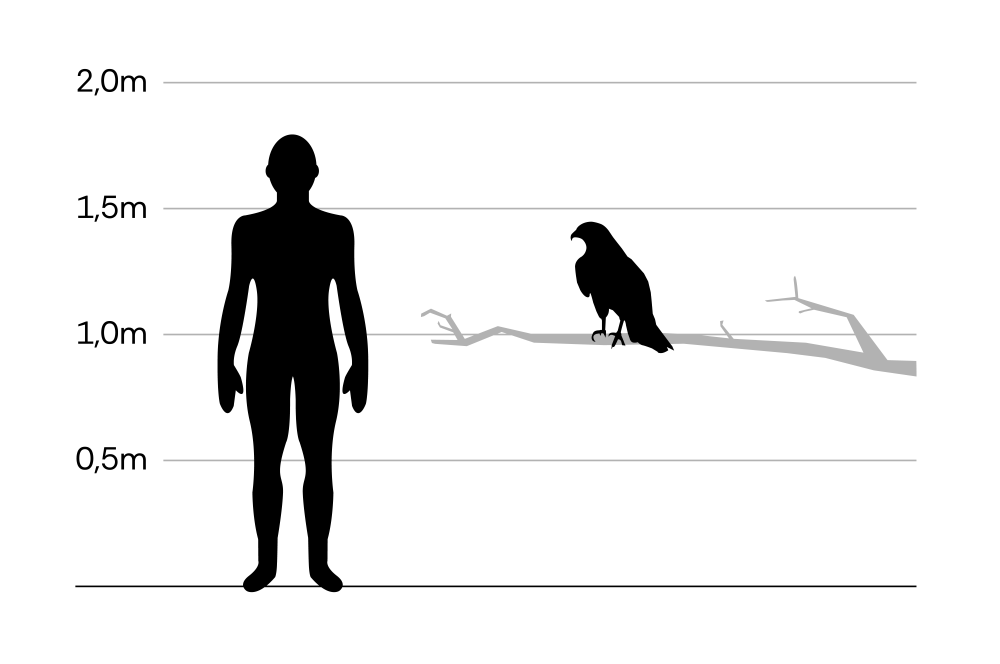
Common buzzard
Buteo buteo
The common buzzard is one of the most common birds of prey in Germany and Austria. The favoured habitat consists of fields, forest edges and avenues. Buzzards are resident birds and are fairly territorial. Breeding pairs can stay together for life. They often hunt from fences and poles in search of prey.
Illegally killed buzzards in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed buzzards in Austria
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
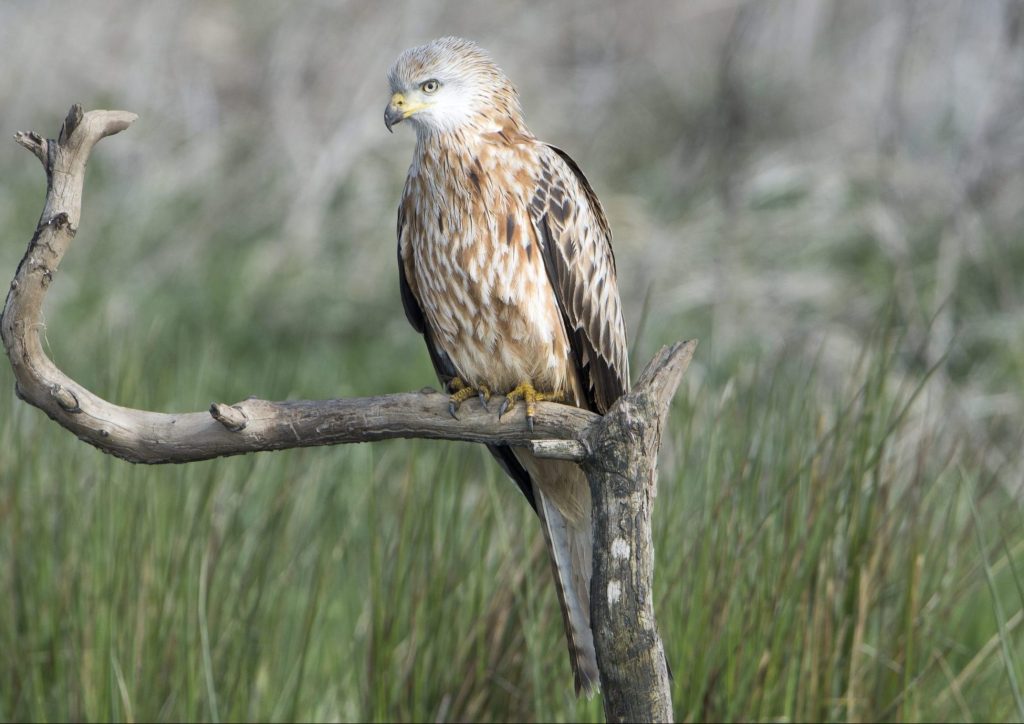

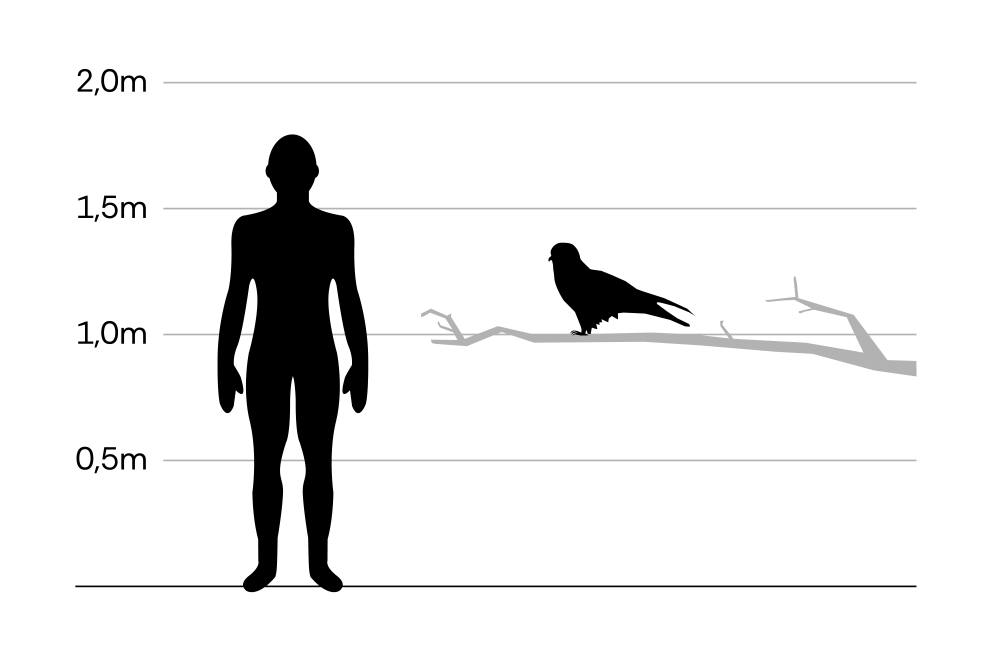
Red kite
Milvus milvus
Red kites are common birds of prey. They inhabit fields, meadows and open cultivated landscapes. While Germany is home to the world’s largest population, Austrian numbers are also constantly growing. Depending on the seasonal food situation, the birds either stay in Germany and Austria or migrate for the winter.
Illegally killed red kites in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed red kites in Austria
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
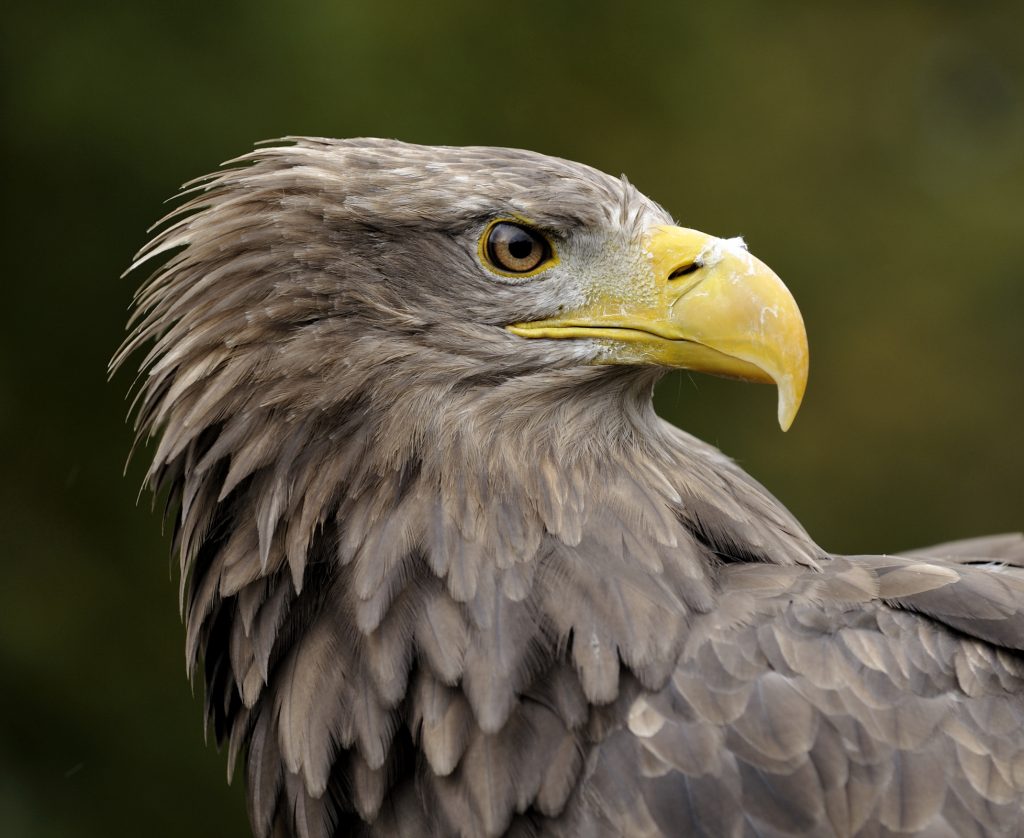

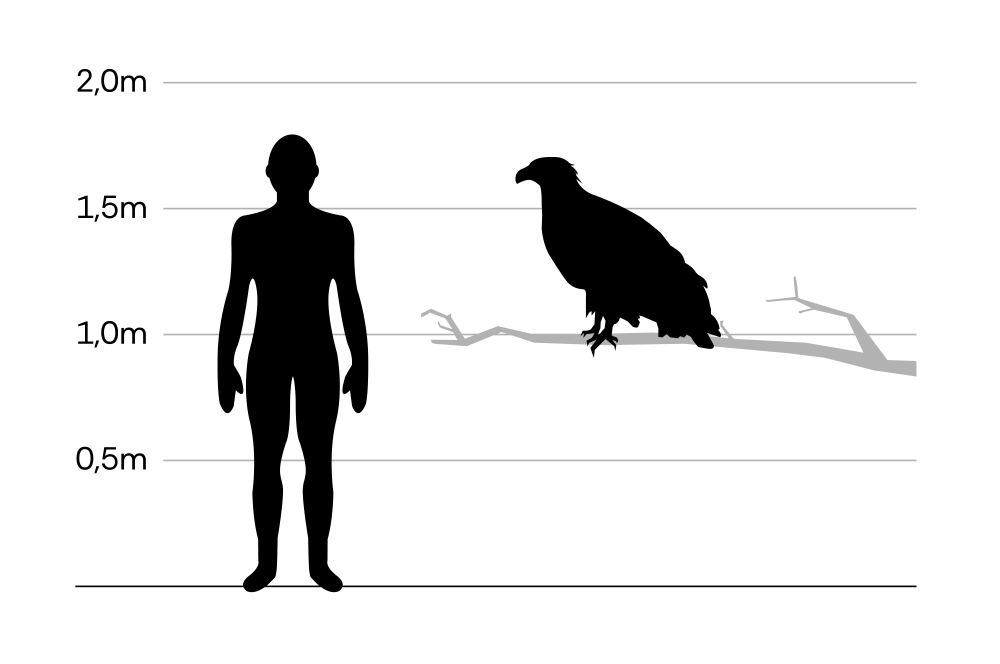
White-tailed eagle (sea eagle)
Haliaeetus albicilla
The white-tailed eagle is the largest European bird of prey and was once widespread throughout most of the continent. It uses rivers, inland lakes and sea coasts for hunting and undisturbed forests as breeding grounds. The animals are resident birds in Central Europe and remain in their territories throughout the winter. There is also a strong influx of Nordic birds at this time.
Sea eagles killed illegally in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Sea eagles killed illegally in Austria
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
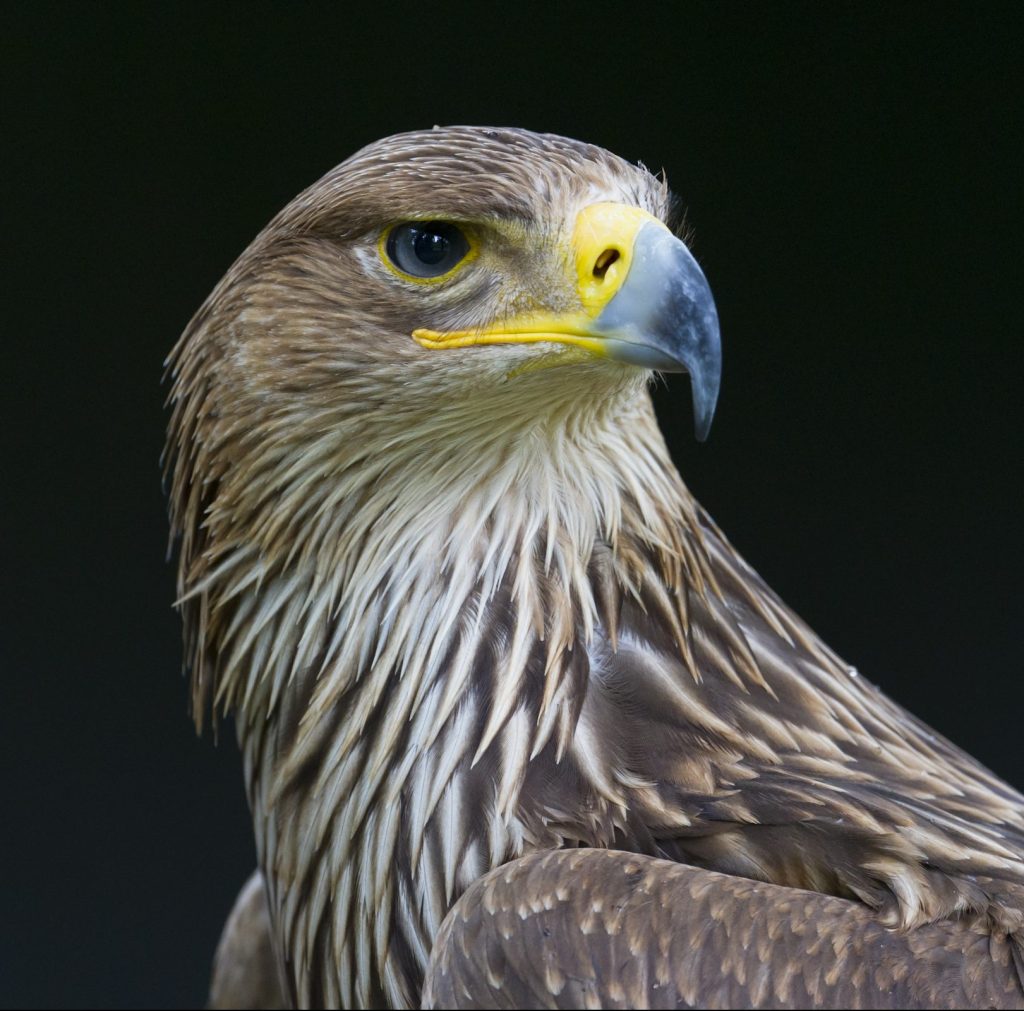

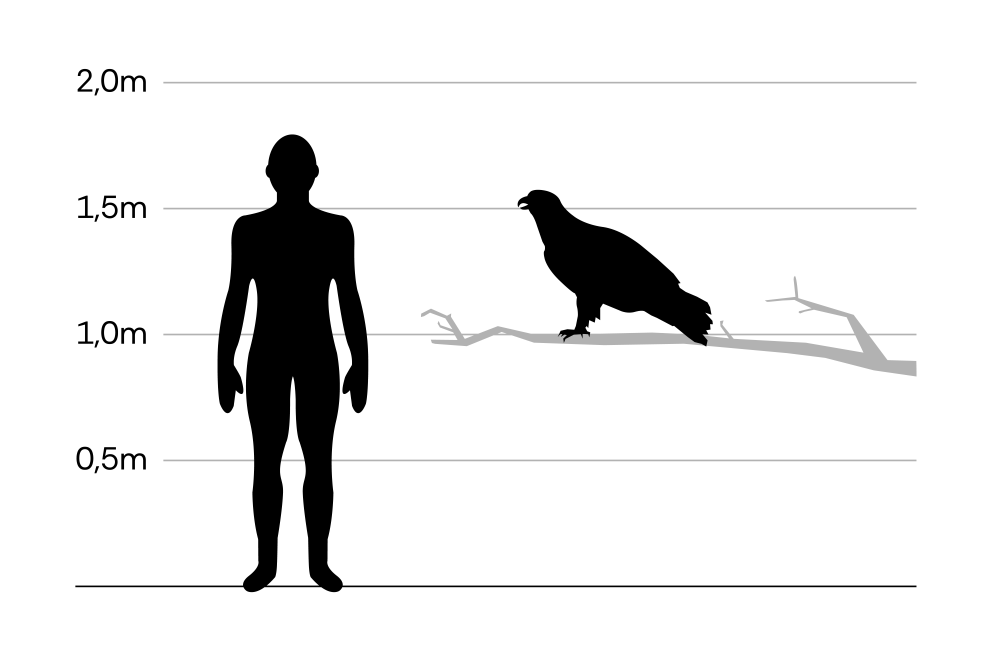
Imperial eagle
Aquila heliaca
The species occurs mainly in the Pannonian Plain (Lower Austria and Burgenland, and further towards south-east Europe). After being wiped out more than 200 years ago, the bird is returning to Austria. Imperial eagles use flat and hilly forests and wind-protected lowlands as breeding habitats. They form permanent marriages and remain in fixed territories.
Imperial eagles killed illegally in Germany
No Data available
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Imperial eagles killed illegally in Austria
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
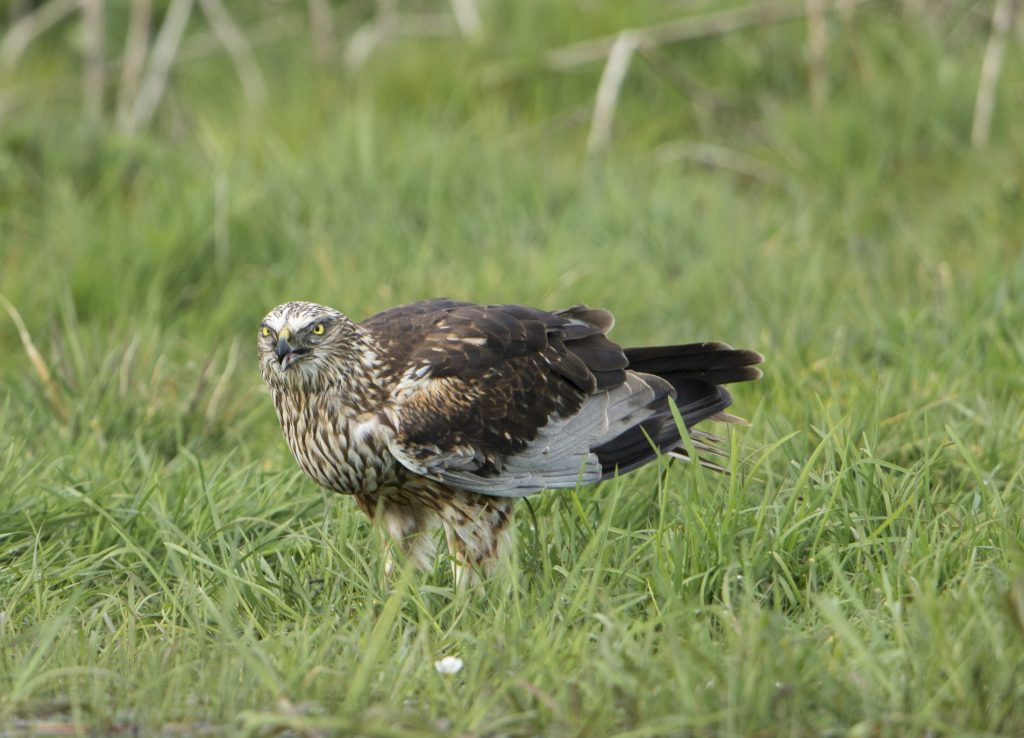

Marsh harrier
Circus aeruginosus
Marsh harriers are a common medium-sized bird of prey species in Germany and partly in Austria. They are not found in Central Europe during the winter, as they are migratory birds. They breed near water and hunt on open land, but rarely form territories. When flying, their upward-pointing wings form a V-shape.
Illegally killed marsh harriers in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegally killed marsh harriers in Austria
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
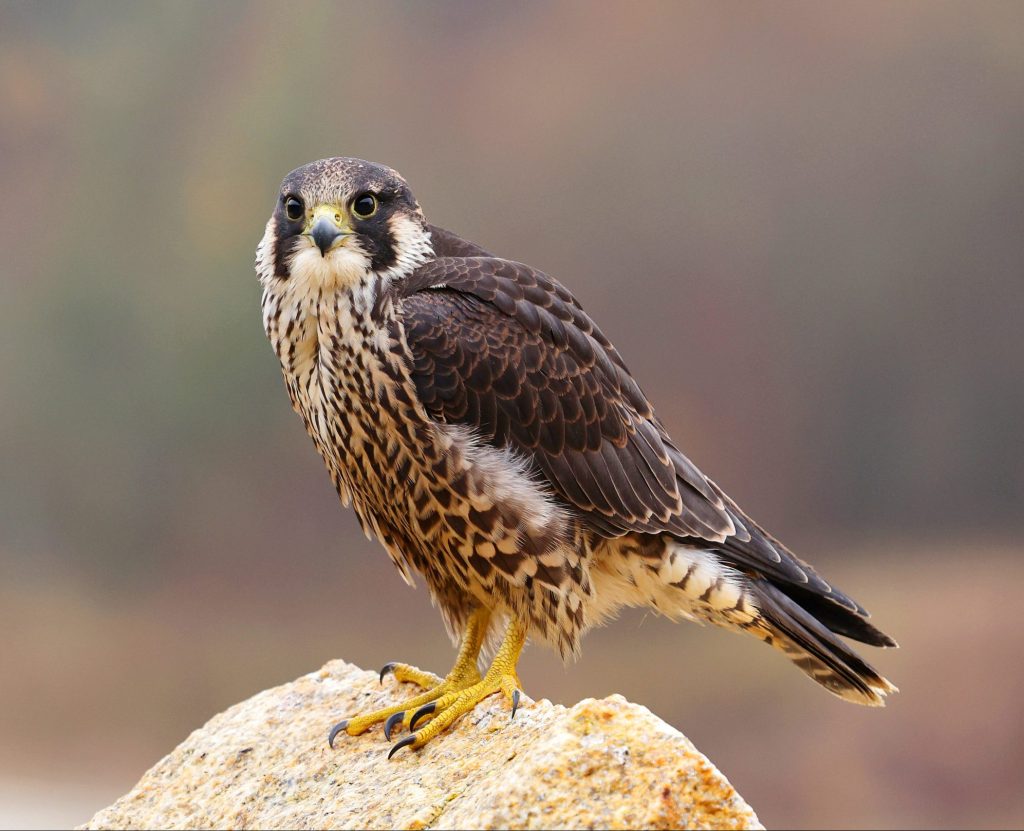
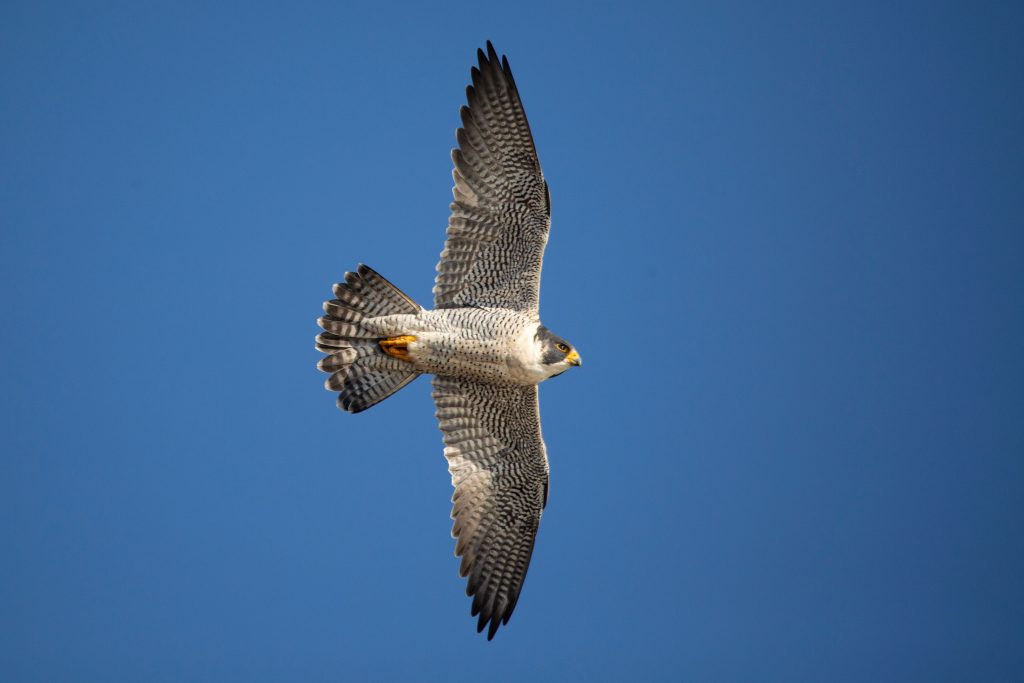


Peregrine falcon
Falco peregrinus
Peregrine falcons are one of the largest falcon species and are found almost all over the world. They are also the fastest animals in the world with a top speed of around 350 km/h. Wooded areas, steep rock faces and man-made structures provide ideal breeding grounds for the animals, while large, open areas are used for hunting. Older animals are resident birds, but juveniles migrate to warmer regions.
Illegally killed peregrine falcons in Germany
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Illegal getötete Wanderfalken in Österreich
Only the actual confirmed cases of illegal killings are listed. The number of unreported cases is likely to be much higher, as many cases are not discovered or reported.
Do you need support with reporting a case?
If so, use our guidelines for combating wildlife crime
Strong Partners










